There are several vital human body systems. In biology, some systems are regarded as more vital than the others but in reality almost every system is integral to normal survival. The more vital systems of the human body are considered to be life inducing systems without which a human body will not be alive.
But even the less vital systems of the human body can have life threatening consequences upon their damage or malfunctioning, albeit to a lesser extent that the more vital ones. Here is a list of the vital systems of the human body.
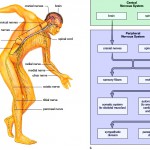
Nervous System
The nervous system comprises of the brain, the spinal cord and the entire network of nerves that run through our body. The function of the nervous system is to gather, transfer and process all kinds of information. It uses nerve cells known as neurons that transmit the information throughout the body. From voluntary actions to involuntary responses, from feeling hungry to the feeling of pain, all signals originate at and are transmitted by the nervous system.
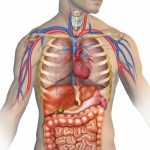
Circulatory System
The circulatory system comprises of the heart, the blood vessels and blood. The circulatory system is tasked with circulating blood, loaded with nutrients and oxygen, throughout the body. This system is also responsible for the beating of the heart, heart rate and blood pressure.
Respiratory System
Respiratory system comprises of the lungs, diaphragm, pharynx, larynx and bronchi. The system is responsible for breathing and in the process absorbs oxygen and releases carbon dioxide from the body.
Digestive System
Digestive system is responsible for processing food and breaking it down for the nutrients to be absorbed by the blood which is then taken to different parts of the body by the circulatory system. The digestive system comprises of the stomach, liver, pancreas, salivary glands, gallbladder and intestines.
Urinary System
The urinary system is tasked with extracting the waste from the system, with assistance from the digestive system, and it excretes the waste out of the body. The system comprises of the kidneys, urinary bladder and urethra.
Muscular System
This system comprises of all the muscles in the human body and is responsible for mobility, structure and form.
Skeletal System
The skeletal system comprises of all the bones and cartilage in the human body and has the same functions as that of the muscles with the exception of joints and spinal cord that have more functions.
Endocrine System
The endocrine system is responsible for secretion the various hormones which all bodily functions require. This system comprises of thyroid, pituitary gland, hypothalamus, pineal gland, adrenal gland, parathyroid and essentially all the endocrine glands.
Reproductive System
The reproductive system comprises of the sex organs in the human body meant for procreation. The organs are ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes, mammary glands, vagina, testes, seminal vesicles, vas deferens and prostate.
Immune / Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system comprises of the blood stream, tissues, lymph and the lymph nodes. The system is also known as immune system because it controls the automatic defence mechanisms of the body and regulates the generation of antibodies.
Integumentary System
The Integumentary system is responsible for protecting the body from external influences. The system comprises of skin, hair and nails.