Congestive heart failure (CHF) is a medical condition that causes your heart to become severely engorged with fluid, resulting in reduced cardiac output and an elevated blood pressure. Without treatment, CHF is fatal within a few months. However, modern medicine has found ways to treat CHF that can prolong the life of patients by several years. In this article, we discuss the symptoms, diagnosis as well as treatments for congestive heart failure.
What is Congestive Heart Failure?
Congestive heart failure is a condition in which the heart has excess fluid and cannot pump blood efficiently. This results in a drop in the blood pressure, which may cause dizziness and fainting when the patient stands up too quickly from a lying position. CHF may be caused by a variety of disorders and injuries, including heart valve diseases and coronary artery disease. Congestive heart failure may occur as the result of a blood vessel disease that causes the heart to become abnormally enlarged. As the condition worsens, heart failure can occur.
Clinical Signs and Symptoms of Congestive Heart Failure
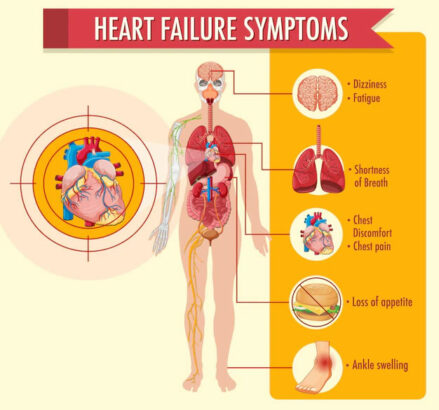
Heart failure causes rapid weight gain and edema (swelling) of the ankles in the first few weeks of being hospitalized. Swollen legs and feet are an important warning sign of heart failure, as they usually do not occur in healthy people. If a patient’s blood pressure drops too low, brain damage may occur. Additionally, the patient may experience breathlessness, fatigue, and leg swelling, signs of heart failure. Other symptoms include shortness of breath, a dry cough, increased fatigue, leg swelling, dizziness, and fluid retention. Patients may also have a change in appetite, although this is often not a symptom of heart failure.
Causes of Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive heart failure occurs when the heart fails to pump blood efficiently. It is commonly caused by heart valve diseases or damage to the heart muscle. A heart valve disease is a condition in which one or more of the heart’s valves does not function properly. An example of this is aortic stenosis, where the aortic valve does not open wide enough to allow the heart to pump blood out of the body.
Prevention and Management Strategies for CHF
If you have heart failure, you will most likely have several medical conditions, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and anemia. Therefore, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. Your doctor may recommend that you take medication, eat a healthier diet, exercise regularly, and maintain a healthy weight. Regular physical activity is an important part of treating and preventing heart failure. It helps to strengthen the heart muscle and reduces the risk of enlarging the heart. You can build up your heart muscle strength by doing aerobic exercises, as well as strength training exercises. You should aim to do at least 30 minutes of physical activity every day.
Cardiac rehabilitation for congestive heart failure
If you have CHF, there is a small chance that your condition may improve or even resolve after an episode of heart failure. If this happens, it is important to maintain good health. This can be done through cardiac rehabilitation, which is a program of physical and emotional support for patients who have experienced a heart attack. Cardiac rehabilitation can improve cardiac function and increase exercise tolerance. It also offers emotional support, guidance, and education. Patients who participate in cardiac rehabilitation have improved quality of life, as well as a lower risk of dying from another heart attack.
Improving cardiac function with medications for CHF
There are several medications that can be used to improve cardiac function and to treat heart failure. These include ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, and angiotensin-receptor blockers. ACE inhibitors are used to treat high blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart failure. Beta blockers are used to treat high blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart failure. Angiotensin-receptor blockers are used to treat high blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart failure.
Congestive heart failure life expectancy
If you want to know how long you can live with congestive heart failure, I’m afraid the news isn’t great. CHF is a life-threatening condition, and the median life expectancy for patients with CHF is only nine to 12 months. However, there are patients who have survived for several years with the condition. You may be able to live a longer, healthier life with help from medication and proper treatment.
Late-stage treatment for CHF: Palliative care and end-of-life care
If your heart failure is advanced, and you are likely to die within a short time, you may want to consider palliative care as an option for end-of-life care. Palliative care is a form of care that focuses on alleviating the symptoms of serious illnesses, relieving the physical, emotional, and spiritual suffering of patients and their loved ones. Palliative care can help patients and their families to cope with a serious illness. This type of care can also be used to provide support for patients who want to discontinue long-term treatment for a serious condition. Palliative care can be provided before or after a patient dies, and it can be provided by physicians, social workers, and nurses.
Summing up
Congestive heart failure is a serious medical condition that affects your heart and can result in heart failure. It is commonly caused by heart valve diseases, damage to the heart muscle, or a combination of these conditions. Heart failure is treated with medications, diet, and exercise to improve cardiac function and increase cardiac output. Patients should also maintain a healthy weight. If your heart failure is advanced, and you are likely to die within a short time, you may want to consider palliative care as an option for end-of-life care.